Based on the price targets, market research, and historical data, set the budgeted prices for each category and subcategory of price variance. The budgeted prices should reflect the ace the investment banking interview financial statements question desired prices that the company wants to charge for its products or services, considering the market conditions, customer value, and competitive situation. The budgeted prices should also be realistic and achievable, and aligned with the strategic objectives of the company.
Both types of variances are crucial for maintaining cost control and ensuring that business operations align with financial goals. Price variance in cost accounting refers to the difference between the actual cost of a product or material and its expected (or standard) cost. This variance helps businesses understand why they may have spent more or less than planned on materials, labor, or services. Various factors, such as market fluctuations, supplier negotiations, or unexpected discounts can result in price variance. By understanding price variance calculation and its causes and effects, businesses can gain valuable insights into their pricing strategies, cost management, and overall financial performance. It enables them to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to optimize pricing and enhance profitability.
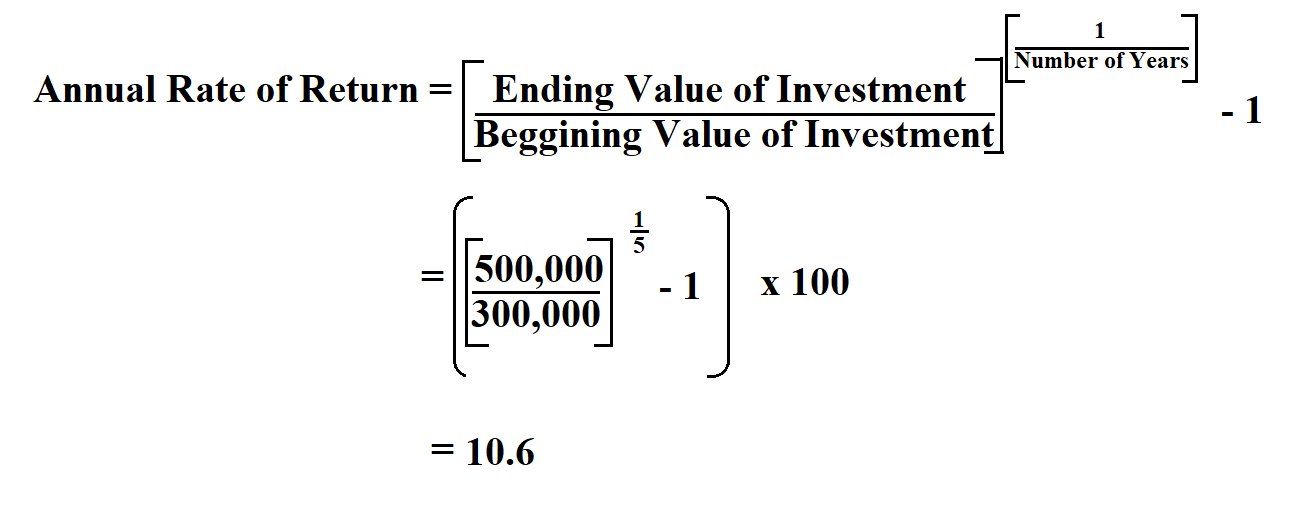
What is Price Variance in Cost Accounting Formula & Calculation
Effective management of sales and labor variances is essential for operational optimization. Companies that actively monitor these variances can make informed decisions that directly impact their bottom line. Adjusting pricing models in response to sales variance data or revising labor strategies based on wage variance insights can lead to improved market competitiveness and financial health. These adjustments are vital for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and profitability in a dynamic economic environment.
Inefficient procurement practices, lack of employee training, and outdated technology can all lead to higher-than-expected costs. Conducting regular internal audits and process reviews can help identify these inefficiencies. Implementing best practices in procurement, investing in employee development, and upgrading technology infrastructure are strategies that can reduce internal sources of variance.
One of the most crucial decisions that entrepreneurs face is how to finance their business… In today’s highly competitive business landscape, the concept of customer-centricity has… Trade credit is a crucial component of working capital management, serving as a financial… In the realm of task management, the ability to accurately estimate the time required for tasks is…
Remember, price variance isn’t just about numbers; it’s a window into your organization’s financial health and operational efficiency. By mastering this concept, you empower yourself to make informed decisions and drive positive change. Sales price and labor cost differences from expectations can significantly affect a company’s profitability and operational smoothness. By assigning appropriate weights, the analysis can focus on the areas that have a higher impact on overall price variance.
Price Variance: Understanding The Difference Between Standard And Actual Prices
Price variance is calculated by subtracting the expected price from the actual price. A positive variance indicates that the actual price is higher than the expected price, while a negative variance suggests that the actual price is lower. By analyzing price variances, businesses can assess the impact of pricing decisions on profitability and make informed adjustments.
Effective optimal choice of entity for the qbi deduction management of price variance, including both purchase price variance and sales price variance, requires continuous monitoring and analysis. The role of the production manager is pivotal in controlling materials price variance, as they ensure that purchasing and production processes align with financial expectations. Purchase price variance refers to the difference between the standard price and the actual price paid for any purchased materials. It covers a broad range of items that a company buys, whether it’s raw materials, components, or finished goods. Conversely, a negative price variance suggests that the actual cost was higher than the standard cost, which might be due to factors like inflation, unexpected price increases, or inefficiencies in procurement. Besides, a purchase manager should only partially depend on variance parameters but instead go into full detail to know the actual reason for the differences in cost.
How to Overcome Common Obstacles and Limitations of Price Variance?
For example, to reduce the negative discount variance, the company can revise its pricing strategy, improve its value proposition, segment its customers, or train its sales force. To increase the positive mix variance, the company can launch new products, enter new markets, target high-value customers, or optimize its distribution channels. One of the key aspects of price variance analysis is to set realistic and achievable price targets for different products, markets, and customers. Price targets are the desired prices that a company wants to charge for its products or services, based on its strategic objectives, market conditions, and customer value.
In these situations, the responsibility lies on the relevant department rather than the sales department. In this section, we delve into the key takeaways and conclusions drawn from our exploration of price variance. By examining the topic from various perspectives, we gain valuable insights into the factors influencing price fluctuations and their implications for businesses and consumers alike.
What is the formula for the materials price variance (MVP)?
- Moreover, the price variance is not limited to cost but can be applied to revenue or selling price.
- Notably, the standard price of an item is determined before the items are purchased.
- A case study conducted on a manufacturing company highlighted the importance of analyzing price variances in raw materials procurement.
- A price variance means that actual costs may exceed the budgeted cost, which is generally not desirable.
What might cause a variance between the standard unit price and the actual price? Quality of product purchased, market issues including unavailability of product or competition for the same materials could all be factors here. For instance, recurring unfavorable variances in material costs might indicate issues with supplier reliability or market volatility. By using data visualization tools, businesses can create charts and graphs that make it easier to spot these patterns. These visual aids can be particularly useful in presenting findings to stakeholders, helping them grasp the significance of the variances and the underlying causes. Businesses must ensure they have reliable records of both standard and actual prices, as well as the quantities purchased.
Thus, the company may pay less for materials than originally anticipated in the budget. This results in a favorable variance because the drop in material prices result in less costs for the manufacturer and increase its profits for the period. From fluctuating material prices to unpredictable supplier rates, keeping track of what you expected to pay versus what you actually paid is challenging.
- Regularly applying the direct material price variance formula and analyzing its outcomes helps in fine-tuning procurement operations.
- There is no way of knowing what the price of oil, steel, or any other commodity will be in the next year.
- Therefore, it is important to have effective strategies and methods to reduce price variance and increase profitability.
- By adopting a holistic view and implementing a combination of these strategies, businesses can navigate price fluctuations and maintain financial stability.
- Understanding price variance is essential for businesses to assess their financial performance, identify potential cost-saving opportunities, and make informed decisions.
- When prices vary, it can impact various areas of a business, including sales, profitability, customer perception, and market competitiveness.
Forrester Recognizes HighRadius in The AR Invoice Automation Landscape Report, Q1 2023
By leveraging this analysis, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost optimization, and revenue maximization. Remember, price variance analysis is a powerful tool that enables businesses to stay competitive and adapt to market dynamics. Different from sales price variance, price variance is the true unit cost of a purchased item, minus its standard cost, multiplied by the number of actual units purchased. It’s used in budget preparation and to determine whether certain costs and inventory levels need to be adjusted. Sales price variance is the difference between the price at which a business expects to sell its products or services and what it actually sells them for.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can optimize costs, enhance decision-making, and maintain a competitive edge. Regularly reviewing and acting upon price variances ensures cost efficiency and competitiveness. The direct material price variance measures the difference between the expected cost accounting equation explanation of materials and the actual cost incurred. To calculate price variance, subtract the actual cost from the standard cost, then multiply the result by the quantity purchased or used. Calculating price variance is an important aspect when it comes to analyzing and interpreting financial data.
Understanding Price variance Calculation is a crucial aspect when it comes to analyzing and evaluating the fluctuations in prices and their underlying causes and effects. In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of price variance calculation, providing insights from various perspectives. A favorable MPV offers that a purchasing department managed to buy the direct materials at economical rates compared to the estimated value. For instance, a purchasing department might have ordered lower quality material to get a lower cost.
These case studies highlight the significance of price variance analysis in various industries and provide practical examples of how businesses can effectively manage and mitigate price variance. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing appropriate strategies, organizations can optimize their pricing decisions and drive sustainable growth. In this section, we will delve into real-world case studies that demonstrate the importance and application of price variance analysis. By examining different perspectives, we can gain valuable insights into the factors influencing price variance and how it impacts businesses. The calculation for direct materials price variance involves subtracting the actual cost of materials from the standard cost, then multiplying by the quantity purchased. Sales price variance measures the difference between the anticipated revenue from product sales and the actual revenue received.